Universum asked over 100,000 Millennial professionals and students, across Asia Pacific, about their ideal employers.
The survey also aimed to find out what attributes they look for when choosing a career/employer. The answer? Achieving work-life balance is now of prime importance. No longer is job stability or competitive pay the number one characteristic that Millennials look for.
The following is a breakdown of the results by country:
Japan
Surveys taken from over 10,000 people, showed the following results:
For business students/professionals, the top choices are All Nippon Airways, Google, and Itochu Corporation, while Mitsubishi Corporation, Apple, Japan Airlines, and Japan International Cooperation Agency are next in line. Other popular companies that value “work-life balance” in Japan include Suntory, Toyota Motors, and Shiseido, in that order.
For engineers, the top ten employers from best to worst are Google, Toyota Motors, Sony, Apple, and Suntry, while Ajinomoto, All Nippon Airways, Hitachi, Shiseido, and Microsoft round out the rest.
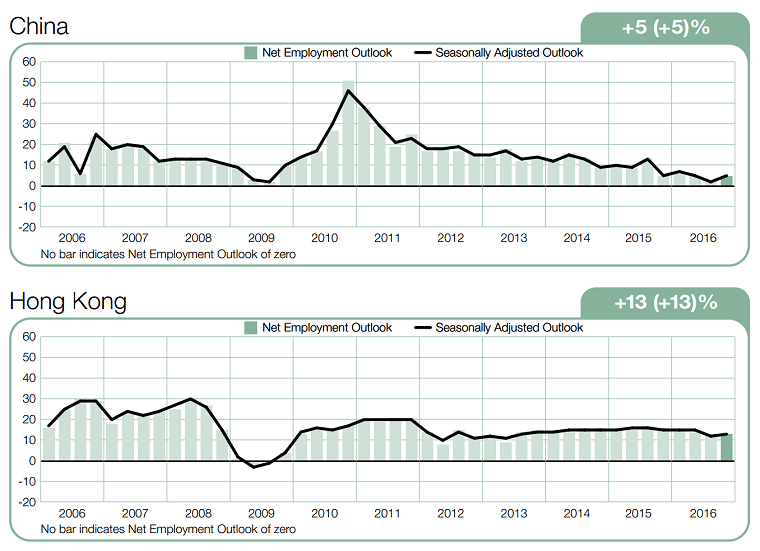
China
For Chinese business students/professionals, the top employers include Alibaba, Ernst & Young, PricewaterhouseCoopers, Bank of China, Huawei, Citi, Deloitte, Apple, and Tencent respectively.
For engineers, their best bet would be, from top to bottom, Huawei, Alibaba, Tencent, Google, and Apple. Following those are Baidu, Microsoft, State Grid Corporation of China, Siemens, and the BMW Group.
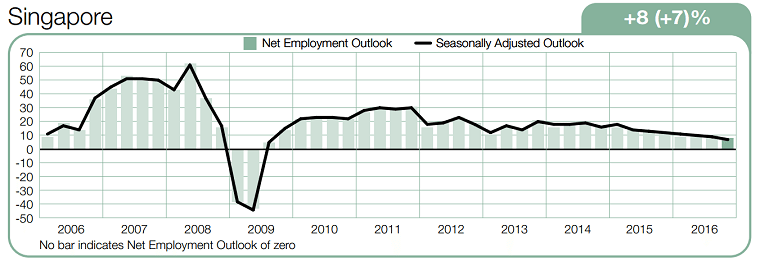
Singapore
For people in Singapore these are the top employers.
- Engineering/Natural Sciences: A*STAR, Google, Singapore Airlines.
- IT: Google, Microsoft, Apple.
- Business: Google, Singapore Airlines, Walt Disney.
- Humanities/Liberal Arts/Education: Walt Disney, Google, Ministry of Education (MOE).
Vietnam
Unilever is the ideal employer for business students/professionals while Google, Vinamilk, and Samsung follow in its footsteps. Following that, the next couple of companies include Coca-Cola, Vietnam Airlines, and AEON Group, with Lotte, Vietcombank and BIDV being last in line.
Engineers opt to go to Samsung, PetroVietnam Group, and FPT, with Viettel, Vinamilk, Google, and Toyota being next in line. Finally, Petrolimex, Microsoft, and Unilever are in the last few places, albeit still some great choices.
Philippines
For Filipino business peple, Google, Ayala Land, and Microsoft are the top three choices, followed by San Miguel Corporation, Samsung, and Nestlé. Finally, Ayala Corporation, ABS-CBN Corporation, Intel, and Shell complete the list.
The perfect jobs for engineers are positions at San Miguel Corporation, Bangko Sentral ng Philipinas, and Google, while other companies include Philippine Airlines and Ayala Corporation. Engineers also like ABS-CBN Corporation, Nestlé, Procter & Gamble and EY (SGV & CO.).
This was the first time this study was done in the Philippines, and the results showed that 55 percent voted for “work-life balance,” and 49 percent chose “to be secure and stable in their jobs.”
Indonesia
The most attractive employers for business minds in Indonesia include Bank Indonesia, Kementerian Keuangan Republik Endonesia, Pertamina, Google, Garuda Indonesia, Kementerian Luar Negeri Republik Indonesia, Otoritas Jasa Keuangan, Unilever, Kementerian Pariwisata and Ekonomi Kreatif, and finally MET Mediatama Indonesia.
The top choices for engineers are Pertamina, Chevron Indonesia, Unilever, Google, Perusahaan Gas Negara, Garuda Indonesia, PLN, and Total E&P.
Here too, the most important career goal is “work-life balance,” coming at 53 percent. A close second is the desire “to be entrepreneurial, creative, or innovative.”
Thailand
Business students/professionals aim to work at Google, Thai Airways International, and PTT. They also have a preference for the Stock Exchange of Thailand, Siam Cement Group, GMM Grammy, Thai Air Asia, and LINE Corporation. The United Nations and Microsoft are also places of interest.
Engineers have a better experience at Google, PTT, Chevron, Siam Cement, Microsoft, EGAT, Thai Airways International, Toyota, BMW Group, and Intel.
Once again, “work-life balance” is chosen as the primary career goal.
Malaysia
In Malaysia Millennials aimed to work for the following companies.
- Engineering: PETROLIAM Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Shell, Sime Darby.
- Business/Commerce: Bank Negara Malaysia, PETROLIAM Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Google.
- Humanities/Liberal Arts/Education: ASTRO, Google, Karangkraf.
- Natural Sciences: PETROLIAM Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Sime Darby, Shell.
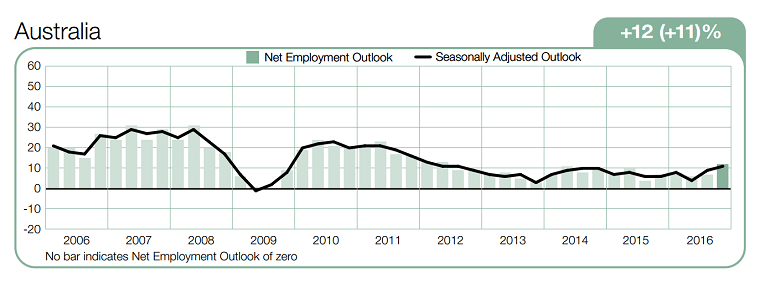
Australia
Those in the Engineering and Natural Sciences fields would like to work for CSIRO, Google and the Government - Federal/Commonwealth.
For Business people, the top employers are Google, Apple and Qantas. While professionals in Humanities, Liberal Arts and Education fields prefer the United Nations and the Government Federal/Commonwealth/State.
It is interesting to see that in varying degrees, “work-life balance” was constantly chosen as the number one criteria when deciding on an employer throughout Asia Pacific. While still a close second overall, “job security” continues to fall as a career goal.
India
In India, these are the most preferred employers.
- Engineering/IT: Google, Microsoft, Apple.
- Business/Commerce: Google, Apple, Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Natural Sciences: Google, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation, Apple.